A cyst is a closed capsule or sac-like structure, usually filled with liquid, semisolid, or gaseous material. The majority of small cysts have no symptoms or signs. However, sometimes the cysts can be felt as a lump or bump in the skin or even in the tissues beneath the skin. Sometimes, these cysts may be painful.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Cysts not associated with the skin but with internal organs may not produce any symptoms if they are small. If the cysts become large and displace or compress other organs or block normal fluid flows in tissues like the liver, pancreas, or other organs, then pain or other symptoms related to those organs may develop.
Cysts usually occur within almost any type of the body’s tissue; they vary in size from microscopic to large structures that can displace internal organs. Although cysts can also refer to any normal bag or sac formation in the body, in this article, we will use the definition stated above and consider it to be an abnormal formation.
Consequently, the cysts discussed below are not normal parts of the body. They have distinct membranes or cyst walls. If the sac is filled with pus, it is usually considered an abscess, not a cyst.
Types of cysts
There are hundreds of different types of cysts. Cysts can occur almost anywhere in the body (for example, on the face, scalp, or back, behind the knee, arm, groin, and within organs like the liver, ovaries, kidneys, or brain). The majority of cysts are benign, but a few may contain malignant cells.
The following lists some of the cyst types that may be found in the body:
- Epidermoid (sebaceous) cyst: usually benign swelling in the skin arising in the sebaceous gland, typically filled with yellowish sebum. These are usually easily seen as they lead to swelling of the skin. If they become large enough, they can be unsightly and cause pain.
- Breast cyst: a fluid-filled sac within the breast. Breast cysts should always be evaluated to assure that they are benign cysts and not other growth.
- Ganglion cyst or synovial cyst: a non-neoplastic soft-tissue collection that may occur in any joint
- Dermoid cyst: an abnormal growth containing epidermis, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands, derived from residual embryonic cells
- Ovarian cyst: an accumulation of fluid within or on the surface of an ovary; also termed adnexal cysts
- PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome): enlarged ovaries due to an endocrine problem that contains several fluid-filled cysts (follicles)
- Baker cyst: a benign swelling of the membranous synovial bursa behind the knee; also known as a popliteal cyst
- Bartholin cyst: formed when a Bartholin gland (at the opening of the vagina) is blocked. A Bartholin cyst can be very painful.
- Arachnoid cyst: a collection of cerebrospinal fluid covered by arachnoid cells and collagen that develops between the surface of the brain in the cranial base or on the arachnoid membrane
- Epididymal cyst: extratesticular spherical cysts in the head of the epididymis
- Labial cyst: any fluid-filled cyst in the labia
- Sebaceous cyst: a small, noncancerous cyst that commonly appears on the torso, neck, and face
- Pilonidal cyst: a cyst that contains hair and skin debris near or on the cleft of the buttocks; also known as jeep driver’s disease
- Nabothian cyst: a mucous-filled cyst on the surface of the cervix
- Pineal cyst: a fluid-filled body in the pineal gland (of the brain)
- Thyroglossal cyst: a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct
- A synovial cyst: also known as a ganglion cyst, is a soft-tissue lump that may occur in any joint
- Branchial cleft cyst: a cyst composed of epithelial cells that arise on the lateral part of the neck due to congenital failure of obliteration of the second branchial cleft
- Choroid plexus cyst: small cysts composed of cerebrospinal fluid trapped by spongy brain cells
- Hydatid cyst: Echinococcus spp. tapeworm (larval stage) surrounded by epithelial cells in an organ
- Corpus luteum cyst: a type of ovarian cyst that may persist after an egg has been released from a follicle
- Colloid cyst: in the brain, a cyst containing gelatinous material
- Mucous cyst: a thin sac containing clear fluid that may be found on the lips, mouth, and occasionally in other areas of the body
- Pancreatic cyst: sac-like pockets of fluid within the pancreas. Technically, they aren’t cysts because they are lined with a scar or inflammatory tissue and therefore they are usually referred to as pseudocysts.
- Testicular cysts: fluid-filled cysts in the testicles
- Thyroid cysts: also called thyroid nodules, they may be fluid-filled or contain some solid components; most are benign but a few may contain malignant components.
- Liver or hepatic cysts: thin-walled cysts that contain fluid. The majority are benign.
- Kidney or renal cysts: walled-off fluid-filled areas within the kidney. Some are congenital (polycystic disease).
- Sinus cysts: abnormal tissue growth, usually in the maxillary sinuses, filled with liquid, air, or semisolid material
- Choroid plexus cysts: are small pinched-off blebs that are formed when the brain is developing the choroid plexus. They contain cerebrospinal fluid.
- Lumbar synovial cyst: a cyst in the lumbar spine that may cause symptoms of spinal stenosis
- Pilar cyst: the common cyst that forms from a hair follicle
- Tarlov cyst: fluid-filled sacs that form on the base of the spine
- Anechoic cyst: any cyst that absorbs sound waves produced by an ultrasound
- Perianal or pilonidal cyst: a cyst usually containing skin debris usually located near the tailbone
- Hemorrhagic cyst: a cyst that contains blood or has internal bleeding
- Arachnoid cyst: cyst containing cerebrospinal fluid that may develop between the brain and the arachnoid membrane
- Maxillary cyst: cysts located in the maxillary sinus area
- Conjunctival cysts: fluid-filled on or under the conjunctiva of the eyes
- Pericardial cysts: uncommon benign congenital abnormality in the medial mediastinum containing clear fluid.
Causes
There are many causes of cyst formation.
The following are some of the major causes of cyst formation:
- Genetic conditions
- Tumors
- Infections
- Errors in embryonic development
- Cellular defects
- Chronic inflammatory conditions
- Blockages of ducts in the body
- Parasites
- Injuries
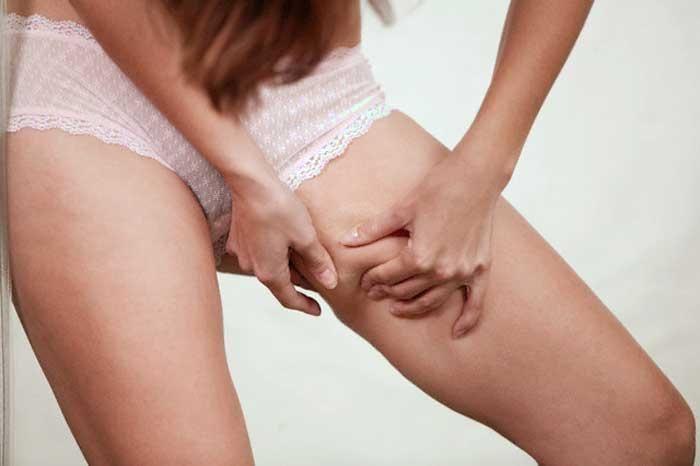
Cysts on inner thigh can be uncomfortable because of the related pain, sheer size (they can grow quite large), and the close-to-the-groin location.
Unlike acne, an inner thigh boil can take weeks to heal; often, they don’t go away for good but lie dormant and then reappear.
Diagnosis
Some cysts are easily palpated by the doctor, especially if the cysts are located in the skin or readily palpable organs, like the thyroid gland. Imaging studies such as ultrasound, X-ray, CAT scans, and MRIs are very useful in finding cysts. In addition, needle biopsies are sometimes used to determine if malignant tissue is associated with a cyst-like structure. In addition, a needle biopsy may be used to reduce the size of the cyst.
Bumps or Cyst on Inner Thigh Causes
There are a number of reasons for cyst on the inner thigh. The first is Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS). Hidradenitis Suppurativa starts as pimple-like cyst on the skin that form where pimples typically don’t appear (the underarms and groin).
A cyst on the inner thigh filled with blood is typical form of HS.
Hair follicles can become blocked and cysts and boils can develop as a result. When hair is pulled or cut at the root, it sometimes curls into itself when it regrows, which means that it’s stuck under the skin and skin cells form layers on top of it. This ingrown hair irritates the area and can form boils or cysts. Some people are more susceptible to this condition than others.
Boils occur as a result of an infection around a hair follicle. They are common and are most often caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, the most common bacteria found on the skin.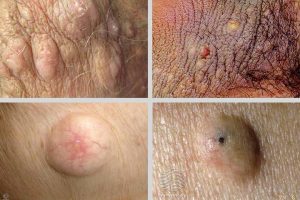
A staph infection on the inner thigh can cause a cyst or boil (furuncle) to appear, and become red, irritated, and painful that could be inflammation.
If the boil (furuncle) is red, painful, contains pus, and the skin surrounding it is warm and painful to the touch, that could be an infection.
Cysts on the inner thigh near the groin in females happen most often because of shaving and waxing.
Jock itch:
This is a fungal infection that occurs mostly in men around the groin, but can spread to the thighs if not treated. It usually looks like a rash with small red bumps and are very itchy.
Tumor:
In rare cases, a cyst on the inner thigh can be a tumor. These cysts grow under the skin and do not present on the surface.
If you notice them spreading quickly, it could mean that the tumor has metastasized.
Folliculitis:
Much like Hidradenitis Suppurativa, folliculitis involves hair follicles which become inflamed as a result of bacterial infection. It typically presents with itching and painful boils on the inner thigh.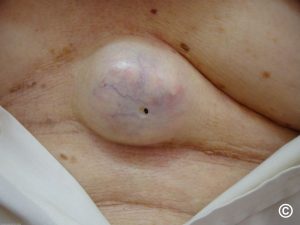
Abscesses:
An abscess on the inner thigh can be caused by the S. Aureus bacteria. It can result in pain, swelling, warmth in the area, redness, and cysts.
Warts:
Dry, red cysts that feel scaly could be warts.
The Difference between a Cyst and Boil or Furuncle
A cyst and a boil (furuncle) look and feel very much the same, except a boil can grow larger and become extremely painful.
A boil is usually caused by a staphylococcus infection which can result in a fever.
The pus in a boil (furuncle) can accumulate massively (so if this happens the fluid will need to be removed).
Never ever pop Cysts or boils on your own, especially if they are extremely large.
Allopathic treatment for cysts
The treatment for a cyst depends on the underlying cause of the cyst and whether or not the cyst is causing the patient problems. According to allopathic theory, many cysts are benign and require no treatment. However, large cysts can result in symptoms due to compression of normal tissue and obstruction of ducts.
Some of these cysts can be treated by simply aspirating the cyst contents through a needle or catheter, thereby collapsing the cyst. Other cysts require surgical removal (some cysts like ovarian cysts can be removed by laparoscopic surgery), especially if there’s any suspicion of malignancy.
In general, cysts that cause symptoms are treated by draining them and/or removing them surgically; allopathic treatment is limited to reducing associated symptoms of their underlying cause(s). Doctors should discuss with patient for the best methods to use to get rid of their cysts.
Homeopathic treatment of Cysts
In Homeopathic treatment the treatment for a cyst also depends on the underlying cause of the cyst and whether or not the cyst is causing the patient problems. According to Homeopathic theory, all cysts are benign and require treatment as soon as it is possible. Because any type and size of cysts can result in other disease(s) and symptoms due to compression of normal tissue, obstruction of ducts and further inflammation and/or infections. With Homeopathy its very simple to treat any type of cyst in very little time period. Here are few medicines explained for cysts treatment:
Graphites
Graphites having a marked action on dissolving the cysts. Like Baryta Carb, it is also a significant medicine for treating sebaceous cyst on the scalp.
Cyst is large and smooth. Itching and marked heat.
Baryta Carb
Baryta Carb is a beneficial medicine for treatment of various kind of cysts and tumours. It is most prominently indicated for cyst on the scalp. Cyst may be sensitive to touch.
Fatty tumours, swollen and hard indurated glands.
Silicea
Silicea is a very effective homeopathic medicine for treating different types of cysts. It possesses a great ability to shrink and dissolve the cysts.
It is also indicated when infection has occurred with abscess formation (pus). The pus is scanty-bad smell. Sebaceous cyst on the scalp, Smooth and appear shiny.
Thuja
To treat many sorts of cyst and tumours, useful to treat sebaceous cyst, cyst in the breast and ovaries, spongy and fatty tumours.
Benzoic acid
Benzoic acid is used for ganglion cysts that are accompanied by dark brown, foul-smelling urine.
Hepar Sulph
Hepar Sulph possesses a great power to manage cases where infection has occurred and abscess has formed.
It works well when there is pus discharge, bloody pus, throbbing or/and splinter like pain. The abscess is tender and sensitive to touch. The skin overlying the abscess is inflamed and appears warm to touch.
Lobelia Inflata
Lobelia Inflata has a tendency to resolve most obstinate cysts. It either makes the cyst dissolve gradually or resolves it by aiding the discharge of its contents.
Calcarea carb
Calcarea carb is used for ganglion cysts on the right side. It treats pain and nerve compression caused by the cyst.
Kali Bromatum
Sebaceous cyst. It treats many types of cyst and tumours (ovarian cyst, fibroids and fatty tumours etc).
P.S: For detailed study please Read the following articles too (just click on the required field/disease):
Bartholin Gland Cyst, Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst, Infected Blackheads, Tiny Red Spots on Skin – Petechiae, Tinea Versicolor or Pityriasis Versicolor Skin…
For consultation; Feel free to whatsapp us or visit our clinic.
P. S : This article is only for doctors having good knowledge about Homeopathy and allopathy, for learning purpose(s).
For proper consultation and treatment, please visit our clinic.
Location, address and contact numbers are given below.
NoN of above mentioned medicine(s) is/are the full/complete treatment, but just hints for treatment; every patient has his/her own constitutional medicine.
To order medicine by courier, please send your details at WhatsApp– +923119884588
 Dr. Sayyad Qaisar Ahmed (MD {Ukraine}, DHMS), Abdominal Surgeries, Oncological surgeries, Gastroenterologist, Specialist Homeopathic Medicines.
Dr. Sayyad Qaisar Ahmed (MD {Ukraine}, DHMS), Abdominal Surgeries, Oncological surgeries, Gastroenterologist, Specialist Homeopathic Medicines.
Senior research officer at Dnepropetrovsk state medical academy Ukraine.
Location: Al-Haytham clinic, Umer Farooq Chowk Risalpur Sadder (0923631023, 03119884588), K.P.K, Pakistan.
Find more about Dr Sayed Qaisar Ahmed at :
https://www.youtube.com/Dr Qaisar Ahmed
https://www.facebook.com/dr.qaisar.dixecosmetics

Comments are closed.